Life cycle of a moth diagram quiz
Moths are like the dusky, fluffy cousins to butterflies. Indeed, they share many things in common – from the general shape of their wings to the way they grow from caterpillars to adults.
The Enchanting Life Cycle of a Moth: A Glimpse Beyond the Butterfly
While the life cycle of a butterfly often captures the imagination of young learners, there is another equally fascinating metamorphosis in the world of insects - the life cycle of a moth. Delving into this captivating transformation, complete with an interactive life cycle of a moth diagram quiz, offers a deeper understanding of the mysteries that nature holds.
Moths vs. Butterflies: Spotting the Difference
Before diving into the life cycle of a moth, it's essential to distinguish between moths and butterflies. Both belong to the order Lepidoptera, but there are subtle differences. Moths usually have a robust, furry body with feathery antennae, while butterflies boast slender bodies and clubbed antennae. Most moths are nocturnal, whereas butterflies are active during the day.
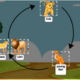
Stage 1: The Egg
The life of a moth, much like a butterfly, begins as a tiny egg. Laid on plants that will serve as food for the emerging caterpillar, these eggs are strategically placed by the female moth to ensure the best chances of survival for the offspring.
Stage 2: The Hungry Caterpillar
From the egg emerges a caterpillar or larva. This stage of the life cycle is all about growth. The caterpillar eats almost continuously, munching on leaves and storing energy for the upcoming transformation. As it grows, it sheds its skin, known as molting, multiple times.
Stage 3: The Cocoon
As the caterpillar reaches the end of its growth phase, it begins the process of pupation. Unlike butterflies that form chrysalises, most moths spin silken cocoons. Hidden inside, away from the prying eyes of predators, the caterpillar undergoes a miraculous transformation.
Stage 4: Emergence of the Adult Moth
After a period within the cocoon, the fully-formed adult moth emerges. This adult, or imago, has fully developed wings and is ready for flight. Its primary purpose now is to find a mate and lay eggs, continuing the cycle for another generation.
Dive into the Interactive Moth Diagram Quiz
For those eager to test their newfound knowledge on the life cycle of a moth, an interactive life cycle of a moth diagram quiz awaits. Engaging and informative, this quiz offers a hands-on approach to learning, allowing kids to visualize and solidify their understanding of this intricate process.
The Importance of Moths in Nature
Moths, much like butterflies, play a crucial role in the ecosystem. They are pollinators for many plants, ensuring the production of seeds and the continuation of various plant species. Furthermore, they serve as a vital food source for birds, bats, and other animals.
In conclusion, the life cycle of a moth offers a fascinating glimpse into the wonders of metamorphosis, often overshadowed by the more commonly studied butterfly. Each stage, from the tiny egg to the majestic adult moth, reveals nature's complexities and the delicate balance of life. By exploring this topic and testing knowledge through interactive means like quizzes, young learners can foster a deeper appreciation for life science and the myriad mysteries it unravels.
Read more
Upon closer inspection, however, moths do bring something new to Nature’s table. They usually have darker-colored wings, and enjoy flying at night rather than the day.
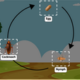
Moth eggs are laid near plants to serve as food for the caterpillars when they hatch. It will take 30 to 40 days for the larva to hatch from its egg. When these caterpillars come out, they first feed on the nutrient-rich protein of their egg’s shells, then move on to leaves and twigs. It molts several times as it grows larger.
Eventually, the caterpillar will enter a protective cocoon spun from its own tough silk. In the safety of this cocoon, it will transform into its adult appearance, growing huge wings, legs, and antennae.
The moth exits its cocoon as a brand-new adult. Its wings will initially feel a little flimsy and weak, but as it feeds and grows stronger, they will harden and become firm enough to fly with.
You can use this life cycle of a moth diagram quiz to review the similarities and differences between butterflies and moths in terms of their life cycles and appearances.